
Monitor the IGBT Temperature of Inverters to Avoid Unexpected Shutdowns
This case study describes the successful implementation of an automated solution to collect IGBT peak temperature data from PV inverters of a specific manufacturer. The solution identifies inverters that exceed a pre-determined temperature threshold, calculates the number of periods of non-compliance and notifies the asset management team on a daily basis. The implementation of this solution has improved operational efficiency, early problem detection and plant maintenance protocols.
CONTEXT
The customer, a leading Independent Power Producer (IPP), managed and operated large-scale photovoltaic plants in Southern Europe. Keeping the IGBT temperature of the inverters within safe operating ranges was crucial to ensuring the performance and durability of the assets.
CHALLENGES
The client faced the following challenges:
- Manual Analysis: Manual analysis of temperature data in MS Excel was inefficient and error-prone, delaying the detection of problems and the implementation of maintenance protocols.
- Time and Effort: Manual data collection and processing required a significant investment of time and effort on the part of the management team.
- Early Detection: The lack of an automated solution delayed the early detection of inverter IGBT temperature problems, leading to unavailability that reduced the assets' productivity.
SOLUTION
Quintas Analytics designed and implemented a complete automated solution to address the challenges mentioned above:
- Advanced Monitoring Platform: A platform was developed that collected, integrated and processed IGBT peak temperature data from inverters.
- Identification of Non-Compliance: Algorithms were implemented to identify inverters and modules that exceeded the defined temperature threshold.
- Calculation of Non-Compliance Periods: The solution calculated the number of periods in which the IGBT temperature of the inverters exceeded the defined threshold.
- Automatic Notifications: Daily notifications were set up for the management team providing a list of inverters showing non-compliance with temperature limits.
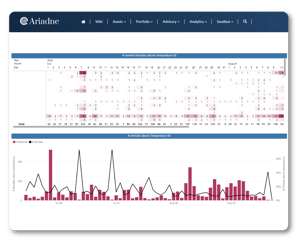
RESULTS AND BENEFITS
Implementing the solution had a positive impact on operations management and the application of maintenance protocols:
1. Efficiency and Time Saving: The automated solution replaced manual analysis using MS Excel, saving the management team time and boosting efficiency.
2. Early Detection: Early identification of inverters with temperature problems enabled a rapid response by the management team.
3. Maintenance Protocols: Daily notifications enabled the appropriate maintenance protocols to be enacted, reducing the risk of serious damage.
4. Asset Optimisation: Early detection and resolution of problems improved asset performance and longevity.
5. Continuous Improvement: The platform enabled ongoing improvements in temperature monitoring and informed management decisions.
CONCLUSIONS
The solution implemented for automated inverter IGBT temperature monitoring and analysis, fault identification and daily notifications proved a success in terms of operational efficiency and enforcing maintenance protocols. The monitoring platform, automated analysis and notifications provided powerful tools for effective and cost-efficient administration by the asset management team. This solution sets a valuable example for the management of similar projects in the solar PV field.
